How does the blockchain job – Imagine an electronic journal that’s shared and upgraded by lots of computer systems. That’s basically a blockchain. Rather than being saved in one area, like a conventional data source, the details is spread out throughout a network, making it clear and exceptionally protected. This dispersed nature is an essential component of what makes blockchain so innovative.
Think of it like a chain of blocks, each consisting of a set of purchases. When a block is filled up, it’s connected to the previous block, developing a solid chain. This sequential document is continuously upgraded and confirmed by the network, producing a tamper-proof and irreversible background. This is the core of blockchain’s protection– it’s really tough to change previous documents since any type of effort would certainly need transforming every succeeding block in the chain, an almost difficult task.
How are these blocks confirmed? This is where cryptography is available in. Each block has a special code, called a hash, which is an intricate mathematical recap of the purchases within it. If any type of deal within the block is transformed, the hash will certainly likewise transform, informing the network to the modification. This indicates everybody on the network can confirm the honesty of the information. The network after that confirms the block with a procedure called agreement, making sure that all individuals settle on the credibility of the purchases.
Here’s a streamlined break down of the procedure:
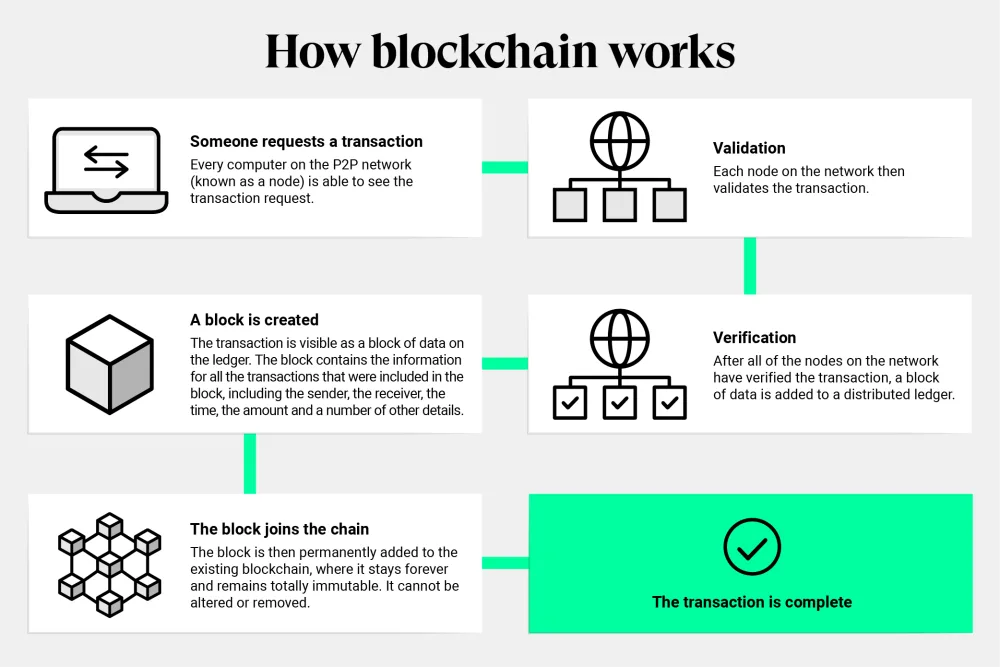
- Transaction Initiation: Someone launches a deal (e.g., sending out cryptocurrency).
- Transaction Broadcasting: The deal is relayed to the network of computer systems.
- Block Formation: Transactions are organized with each other right into a block.
- Verification and Hashing: The block’s information is confirmed and hashed, producing a special code.
- Consensus: The network settles on the block’s credibility (e.g., making use of proof-of-work).
- Block Addition: The confirmed block is contributed to the blockchain, connecting it to the previous block.
Example: Imagine an electronic invoice for every single deal used Bitcoin. Each invoice is contributed to a block, which block is completely connected to the previous block. This chain can not be damaged without transforming each and every single invoice after it, making it exceptionally protect. It’s like a shared, continuously upgraded, and very protected journal.
Famous Entities Related to Blockchain:
- Bitcoin: One of the earliest and most popular cryptocurrencies improved a blockchain.
- Ethereum: A system that makes it possible for the development of decentralized applications (dApps).
- Ripple: A real-time gross negotiation system (RTGS) that makes it possible for quick and protected global cash transfers.
This in-depth description ideally clears up exactly how a blockchain features. It’s an effective innovation with a wide variety of possible applications, from money to provide chain monitoring and past. Recognizing the principles is critical to understanding its possible and effect.
